https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576
# 코드
import sys
from collections import deque
M, N = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
graph = []
for _ in range(N):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
q = deque()
num = 0
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if graph[i][j] == 1:
q.append([i, j])
def bfs():
while q:
dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
x, y = q.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
if 0 <= nx < N and 0 <= ny < M and graph[nx][ny] == 0 :
graph[nx][ny] = graph[x][y] + 1
q.append([nx, ny])
bfs()
for i in graph:
for j in i:
if j == 0 :
print(-1)
exit()
else :
num = max(num, max(i))
print(num-1)
## 2차원 배열
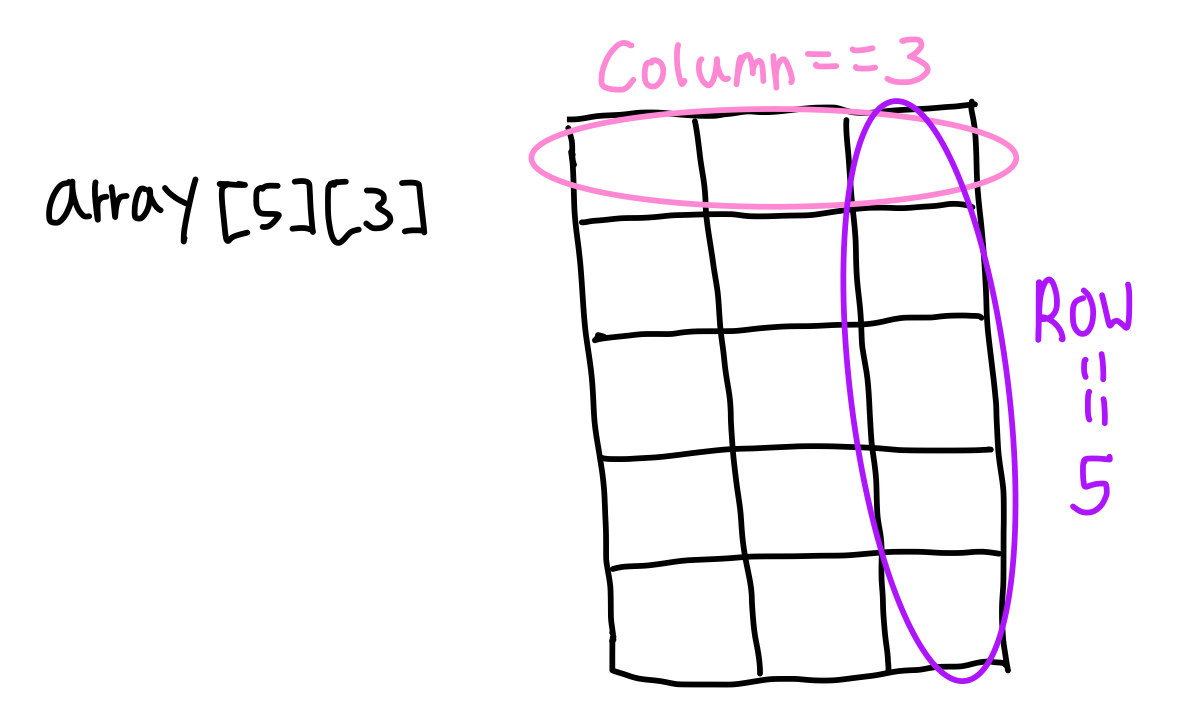
2차원 배열을 선언 시, array[가로수][세로수]다. 헷갈리지 말자.
### BFS 로직
토마토가 익은 위치를 큐에 저장
=> 익은 토마토 위치를 기준으로 상,하,좌,우 모두 탐색
=> 그 위치의 값이 0이라면 이전 값에서 1을 계속 더해주기
=> 큐에 이동한 위치 저장
💭 왜 이전 값(graph[x][y])에서 + 1을 했을까?
=> 이전 값에서 계속 + 1을 해준 값은 토마토가 모두 익을 때까지의 날짜를 구하는데 이용되기 때문이다.
728x90